For information on the optional products required to use this function, see "Optional Products Required for Each Function."
IPSec is a protocol for ensuring the security of IP packets sent and received over an IP network by protecting it from threats such as theft, modification, and impersonation. IPSec is applied for TCP packets, UDP (User Datagram Protocol) packets, and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets. The reason why IPSec is superior to other security protocols is that since it adds security functions to IP, the basic protocol of the internet, it does not depend on the application software and network configuration.
This section describes the procedure for creating a security policy to set IPSec communications, using the control panel of the machine. A security policy registers the settings for IPSec, such as the packets to process with IPSec, and the algorithm to use for authentication and encryption. A logical connection established for traffic by conducting negotiations according to an IPSec security policy is called an IPSec SA (Security Association).
The features of the IPSec used by the machine are as follows.
Since the IPSec of the machine only supports the transport mode, authentication and encryption is only applied to the data part of the IP packets.
At least one of the following methods must be set for the machine. You cannot set both methods at the same time.
AH (Authentication Header)
A protocol for certifying authentication by detecting modifications to the communicated data, including the IP header. The communicated data is not encrypted.
A protocol for certifying authentication by detecting modifications to the communicated data, including the IP header. The communicated data is not encrypted.
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload)
A protocol that provides confidentiality via encryption while certifying the integrity and authentication of only the payload part of communicated data.
A protocol that provides confidentiality via encryption while certifying the integrity and authentication of only the payload part of communicated data.
Supports IKEv1 (Internet Key Exchange version 1) for exchanging keys based on ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol). IKE includes two phases; in phase 1 the SA used for IKE (IKE SA) is created, and in phase 2 the SA used for IPSec (IPSec SA) is created.
To set authentication with the pre-shared key method, it is necessary to decide upon a pre-shared key in advance, which is a keyword (24 characters or less) used for both devices to send and receive data. Use the control panel of the machine to set the same pre-shared key as the destination to perform IPSec communications with, and perform authentication with the pre-shared key method.
To select authentication with a digital signature, a CA certificate (X.509 certificate) must be registered for bilateral authentication of the IPSec destination. For information on installing the CA certificate using the Remote UI, see "Installing a CA Certificate." For information on registering the installed CA certificate file, see "Registering a Key Pair File and Server Certificate File Installed from a Computer."
The types of key pair and certificate that can be used for authentication with the digital signature method are indicated below.
RSA algorithm
PKCS#12 format key pair
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you want to register multiple security policies when setting the Main mode and pre-shared key authentication method in the IKE Settings screen, the following restrictions apply.
Pre-shared key method key: when specifying multiple remote IP addresses to which a security policy is to be applied, all shared keys for that security policy are identical (this does not apply when a single address is specified).
Priority: when specifying multiple remote IP addresses to which a security policy is to be applied, the priority of that security policy is below security policies for which a single address is specified.
|
This section describes the procedure for registering a new security policy.
|
NOTE
|
|
You can register up to 10 security policies. The registered security policies are displayed in order of their priority.
|
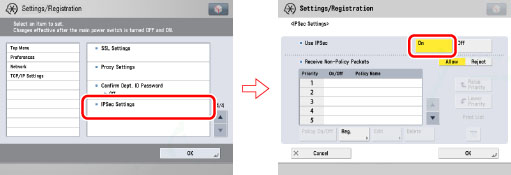
1.
On the TCP/IP Settings screen, press [IPSec Settings] → select [On] for <Use IPSec>.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you set <Use IPSec> to 'On', the machine will not enter a complete Sleep mode.
|
2.
In <Receive Non-Policy Packets>, specify the following settings → press [Reg.].
|
[Allow]:
|
Allows the sending/receiving of packets that are not encrypted because they do not correspond to the security policy set on the IPSec Settings screen, in plain text.
|
|
[Reject]:
|
Rejects the sending/receiving of packets that do not correspond to the security policy set on the IPSec Settings screen.
|
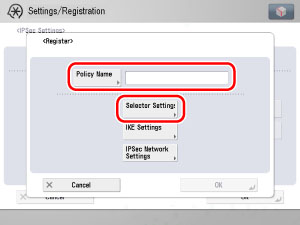
3.
Enter the security policy name to register in [Policy Name] → press [Selector Settings].
4.
On the Selector Settings screen, specify the local IP address to apply the registered security policy to.
When receiving IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the destination IP address in the packets matches the local IP address specified in this procedure. When sending IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the source IP address in the packets matches the local IP address specified in this procedure.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If the link local address is set to a local IP address in this procedure for IPSec communication, the remote IP address set in step 5 should be a link local address.
|
Select [All IP Addresses] for <Local Address>.
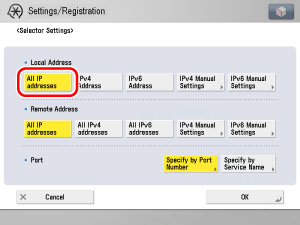
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the IPv4 Address Held By the Machine:
Select [IPv4 Address] for <Local Address>.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the IPv6 Address Held By the Machine:
Select [IPv6 Address] for <Local Address>.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Specified IPv4 Address or IPv4 Network Address:
Select [IPv4 Manual Settings] for <Local Address> → specify a single IPv4 address or range of IPv4 addresses. Also specify the subnet.
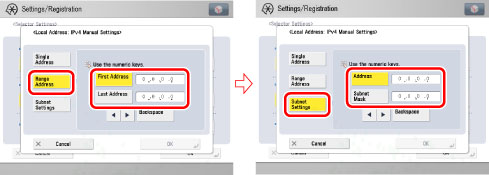
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Specified IPv6 Address or IPv6 Network Address:
Select [IPv6 Manual Settings] for <Local Address> → specify a single IPv6 address or range of IPv6 addresses. Also specify the IPv6 address and prefix length.
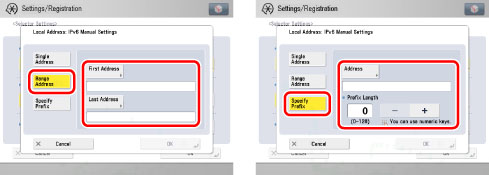
5.
On the Selector Settings screen, specify the remote IP address to apply the registered security policy to.
When receiving IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the source IP address in the packets matches the remote IP address specified in this procedure. When sending IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the destination IP address in the packets matches the remote IP address specified in this procedure.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If the remote IP address is set to a local IP address in this procedure for IPSec communication, the local IP address set in step 4 must be a link local address.
|
Select [All IP Addresses] for <Remote Address>.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to All IPv4 Addresses Held By the Machine:
Select [All IPv4 Addresses] for <Remote Address>.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to All IPv6 Addresses Held By the Machine:
Select [All IPv6 Addresses] for <Remote Address>.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Specified IPv4 Address or IPv4 Network Address:
Select [IPv4 Manual Settings] for <Remote Address> → specify a single IPv4 address or range of IPv4 addresses. Also specify the subnet.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Specified IPv6 Address or IPv6 Network Address:
Select [IPv6 Manual Settings] for <Remote Address> → specify a single IPv6 address or range of IPv6 addresses. Also specify the IPv6 address and prefix length.
6.
On the Selector Settings screen, specify the destination port to apply the registered security policy to.
When receiving IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the destination port in the packets matches the port number specified in this procedure. When sending IP packets, the registered security policy is applied if the source port in the packets matches the port number specified in this procedure.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Local Port and Remote Port Specified By Port Number:
Select [Specify by Port Number] for <Port>.
On the Specify by Port Number screen, set the local port and remote port.
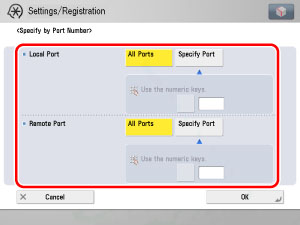
[All ports]: Select to specify all the local ports or all the remote ports.
[Specify Port]: Select to specify a single local port or remote port according to the port number.
Applying a Security Policy to the IP Packets Received from and Sent to the Port Specified By Assigned Application:
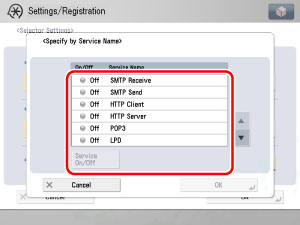
Select [Specify by Service Name] for <Port>.
On the Specify by Service Name screen, select a displayed service name → press [Service On/Off].
7.
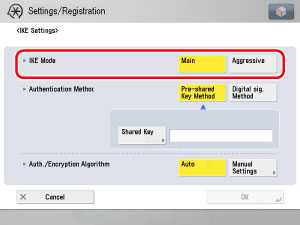
On the Register screen, press [IKE Settings] → select the mode to use for IKE phase 1.
|
[Main]:
|
If you set the Pre-Shared Key Method, the ID for sending is fixed to the IP address.
|
|
[Aggressive]:
|
This mode is simplified version of the Main mode. The part related to the authentication is not encrypted. Any types of ID can be used for conducting negotiations. Also, you cannot conduct negotiations of DH Group.
|
[Main]: Select to set the Main mode. This mode has strong security because the IKE session itself is encrypted.
[Aggressive]: Select to set the Aggressive mode. This mode speeds up IKE sessions because they are not encrypted.
8.
On the IKE Settings screen, specify the authentication method to use for IKE phase 1.
If you want to select the pre-shared key method, prepare a pre-shared key. To select a digital signature method, register the CA certificate in advance (see "Registering a Key Pair File and Server Certificate File Installed from a Computer."), and install the key pair file and certificate file. (see "Installing a Certificate File.")
Press [Pre-shared Key Method] → [Shared Key] for <Authentication Method> → enter the pre-shared key.
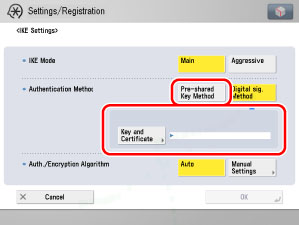
Press [Digital Sig. Method] → [Key and Certificate] for <Authentication Method>, select the key pair you want to use → press [Set as the Default Key] to register the key pair to use for IPSec.
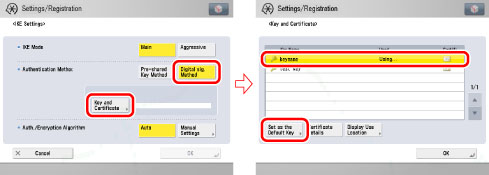
You cannot set to use "Device Signature Key" or "AMS" (key pair for access restrictions).
|
NOTE
|
|
It is necessary to use the Remote UI to delete a key pair registered for IPSec. (See "Installing/Checking/Erasing a User Signature Certificate and Key Pair.")
You can check the content of a certificate by selecting a key pair on the Key and Certificate screen, and pressing [Certificate Details]. On the Certificate Details screen, you can press [Certificate] to verify the certificate.
You can check what a key pair is being used for by selecting a key pair with 'Using' displayed for <Used> on the Key and Certificate screen, and pressing [Display Use Location].
|
9.
On the IKE Settings screen, select the algorithm for the authentication and encryption to use for IKE phase 1.
Select [Manual Settings] for <Auth./Encryption Algorithm> → specify the authentication and encryption algorithm to apply to the IKE SA.
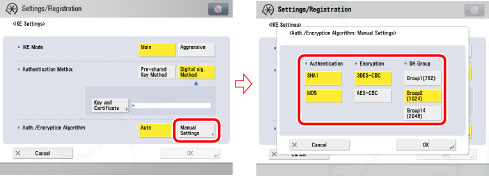
[SHA1] for <Authentication>: Select to set SHA1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) for the authentication algorithm. 160-bit hash values are supported.
[MD5] for <Authentication>: Select to set MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5) for the authentication algorithm. 128-bit hash values are supported.
[3DES-CBC] for <Encryption>: Select to set 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard) for the encryption algorithm, and CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) for the encryption mode. 3DES takes longer to process because it performs DES three times, but enables increased encryption strength. CBC links the encryption result of the previous block with the next block to make it harder to decipher the encryption.
[AES-CBC] for <Encryption>: Select to set AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for the encryption algorithm, and CBC for the encryption mode. AES supports encryption keys with a key length of 128, 192, or 256 bits. As the supported key lengths are long, it enables increased encryption strength. CBC links the encryption result of the previous block with the next block to make it harder to decipher the encryption.
[Group1(762)] for <DH Group>: Select to set Group 1 for the DH (Diffie-Hellman) key exchange method. In Group 1, 762-bit MODP (Modular Exponentiation) is supported.
[Group2(1024)] for <DH Group>: Select to set Group 2 for the DH key exchange method. In Group 2, 1024-bit MODP is supported.
[Group14(2048)] for <DH Group>: Select to set Group 14 for the DH key exchange method. In Group 14, 2048-bit MODP is supported.
Select [Auto] for <Auth./Encryption Algorithm>.
The priority for the authentication and encryption algorithms is indicated below.
|
Priority
|
Authentication Algorithm
|
Encryption Algorithm
|
DH Key Exchange Method
|
|
1
|
SHA1
|
AES (128-bit)
|
Group 2
|
|
2
|
MD5
|
||
|
3
|
SHA1
|
AES (192-bit)
|
|
|
4
|
MD5
|
||
|
5
|
SHA1
|
AES (256-bit)
|
|
|
6
|
MD5
|
||
|
7
|
SHA1
|
3DES
|
|
|
8
|
MD5
|
10.
On the Register screen, press [IPSec Network Settings] → specify the SA validation time and validation type, and PFS (Perfect Forward Security).
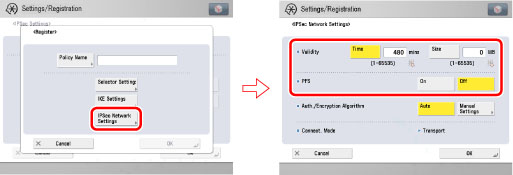
[Time] and [Size] for <Validity>: Specify the validation period for the generated IKE SA and IPSec SA. In IPSec communications to which a valid security policy is applied, packets can be sent and received without conducting key exchange negotiations. Make sure to set either [Time] and [Size]. If you set both, the SA becomes invalid when the value set for either [Time] or [Size] is reached.
[On] for <PFS>: If you enable the PFS function, you can increase the confidentiality because even if one encryption key is exposed to a third party, the problem does not spread to other encryption keys.
[Off] for <PFS>: If you disable the PFS function, if one encryption key is exposed to a third party, other encryption keys may be able to be guessed. If you set <PFS> to 'On', the destination for PFS communication must also have PFS enabled.
11.
On the IPSec Network Settings screen, select the algorithm for the authentication and encryption to use for IKE phase 2.
Select [Manual Settings] for <Auth./Encryption Algorithm>.
Set the ESP authentication/encryption method, or the algorithm for the AH authentication method.
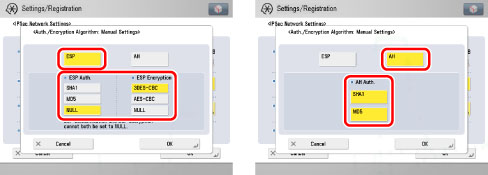
[SHA1] for <ESP Auth.>: Select to set SHA1 as the algorithm for the ESP authentication method. 160-bit hash values are supported.
[MD5] for <ESP Auth.>: Select to set MD5 as the algorithm for the ESP authentication method. 128-bit hash values are supported.
[NULL] for <ESP Auth.>: Select to not set the algorithm for the ESP authentication method.
[3DES-CBC] for <ESP Encryption>: Select to set 3DES for the ESP encryption algorithm, and CBC for the encryption mode. 3DES takes longer to process because it performs DES three times, but enables increased encryption strength. CBC links the encryption result of the previous block with the next block to make it harder to decipher the encryption.
[AES-CBC] for <ESP Encryption>: Select to set AES for the ESP encryption algorithm, and CBC for the encryption mode. AES supports encryption keys with a key length of 128, 192, or 256 bits. As the supported key lengths are long, it enables increased encryption strength. CBC links the encryption result of the previous block with the next block to make it harder to decipher the encryption.
[NULL] for <ESP Encryption>: Select to not set the algorithm for the ESP encryption method.
[SHA1] for <AH Auth.>: Select to set SHA1 as the algorithm for the AH authentication method. 160-bit hash values are supported.
[MD5] for <AH Auth.>: Select to set MD5 as the algorithm for the AH authentication method. 128-bit hash values are supported.
Select [Auto] for <Auth./Encryption Algorithm>.
The ESP authentication/encryption methods are set. The priority for the authentication and encryption algorithms is indicated below.
|
Priority
|
Algorithm for ESP Authentication Method
|
Algorithm for ESP Encryption Method
|
|
1
|
SHA1
|
AES (128-bit)
|
|
2
|
MD5
|
|
|
3
|
SHA1
|
AES (192-bit)
|
|
4
|
MD5
|
|
|
5
|
SHA1
|
AES (256-bit)
|
|
6
|
MD5
|
|
|
7
|
SHA1
|
3DES
|
|
8
|
MD5
|
This section describes the procedure for changing the settings of a registered security policy. It also describes the procedure for enabling a security policy.
1.
On the TCP/IP Settings screen, press [IPSec Settings] → perform the following.
Select the security policy → press [Policy On/Off].
Select the security policy → press [Raise Priority] or [Lower Priority].
|
NOTE
|
|
You can press [Print List] to print a list of the security policies and confirm their priorities.
|
Select the security policy → press [Delete].
Select the security policy → press [Edit].
Change the required items on the Edit screen.
For more information on each setting, see "Registering a Security Policy."